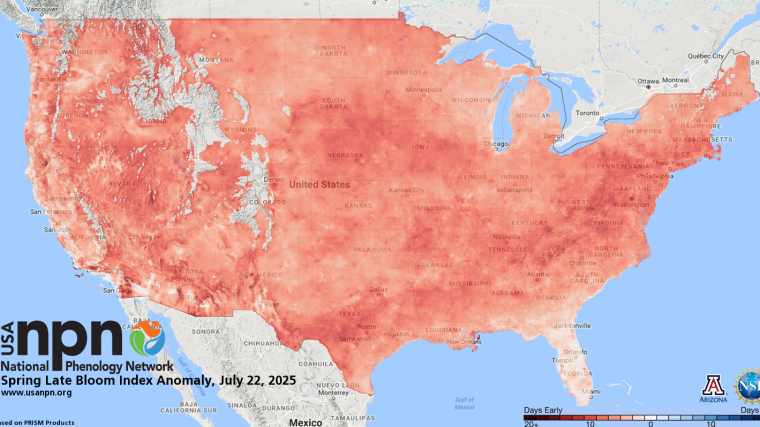
Introducing the Late Bloom Index!
We are excited to unveil another new index of spring – the Late Bloom Index!

We are excited to unveil another new index of spring – the Late Bloom Index!




March 17-21, 2025 is Phenology Week - a virtual celebration of the seasonal cycles of plants and animals. The purpose of Phenology Week is to celebrate YOU, our Nature's Notebook observers, Local Phenology Programs, and partners! We'll have webinars, awards, daily challenges, observer stories, and more.
Share Phenology Week Content on your social media! Our media kit contains daily activities to share with your community!
The Phenophase Primer for Flowering Plants: Understanding Plant Phenophases for Nature's Notebook, is finally here!

Each year, people gather at Gobbler's Knob in Pennsylvania to hear Punxsutawney Phil's prediction of what the next six weeks of weather will bring. This year, Phil predicted six more weeks of winter! But what does the science say?


USA-NPN Director Theresa Crimmins' first book, Phenology, is available now on Amazon, Barnes and Noble, Books a Million, and more. Use code READMIT20 for 20% off orders throug
